The web browser or internet browser has two main elements: the front end, which is the user interface we interact with, and the back end, which is invisible but essential for rendering and generating the webpage.
The browser needs the web address known as Uniform Resource Locator (URL) to receive and render the website elements for generating the web page.
In this guide, I have shared written instruction about:
The Role of HTTP in Web Browser
However, when it comes to performing their primary task of retrieving and displaying information, uniformity is an element. Every bit of data transferred during this process follows the HyperText Transfer Protocol.
HTTP governs how a particular piece of information, be it text, images, or any other file, should be transmitted to the web. In other words, it acts as a foundation stone for any data exchange across the web.
Webpages in HTML Format with Necessary Scripts
On the other hand, the web pages you access via your desired browser have been written in HyperText Markup Language. It is, again, a standard language that every site across the web needs to follow.
All the rules have been written in the HTML and CSS specifications which the World Wide Web Consortium maintains.
Your browser wouldn’t understand the standard text; it must be supplied with all the HTML information.
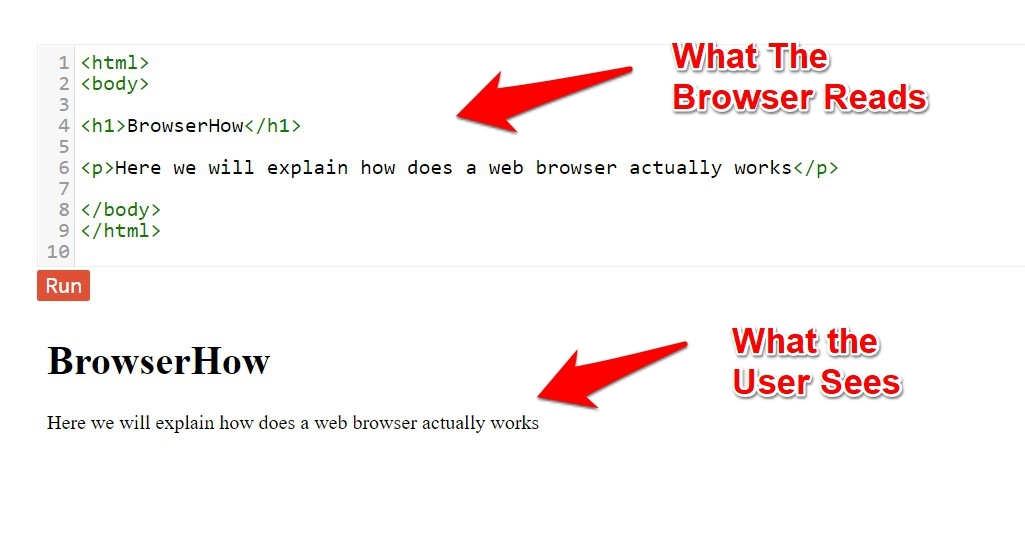
So rather than the plain text you see in the front end, the browser is primarily interested in whatever is happening behind the scenes, i.e., the content within the HTML, Head, Body, and other such tags.
Use of Browser’s Rendering Engine to Display a Page
However, they wouldn’t be interested in this HTML data; instead, they need to get hold of the UI element of the associated data to act upon. This is where a browser’s rendering engine comes into the picture.
As soon as it gets hold of the required resource from a webpage, the engine translates that data to a user-understandable format, and hence you can see the desired site, image, or video.
By default, these engines deal with XML and HTML contents effectively, but their domain could be expanded using third-party add-ons.
Furthermore, different browsers use different types of rendering engines. For example, Firefox uses Gecko; Safari uses WebKit, whereas Chrome uses a fork of WebKit (Blink).
Unique URL for Every Webpage
However, how would they be identifiable with such a plethora of information across the web? To provide a unique identity to each element across the web, they are assigned a unique address. This is also known as the Uniform Resource Locator (URL).
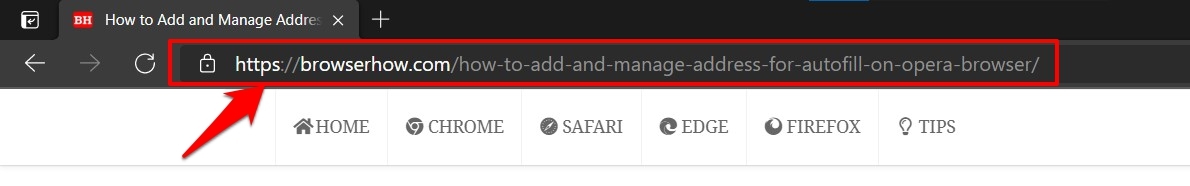 So every website you see, including an image, video, or document, all have been assigned a unique URL. You need to click on that link, and you will then be able to access it with just a single click.
So every website you see, including an image, video, or document, all have been assigned a unique URL. You need to click on that link, and you will then be able to access it with just a single click.
The Need for Uniformity?
In all of these, you might have witnessed one key thing- there is a common framework specified that each browser needs to be in line with.
For example, HTTP takes care of the data transmission; websites follow the HTML, which is governed by the W3C body. So what was the need for this consistency?
Well, there is a plentitude of information spread across the web, belonging to different world regions. If every browser followed its rules, then a lack of uniformity would have made it difficult for the users to understand the information they were trying to retrieve.
But by maintaining a consistent workflow, every user can get the same information from any device, be it in any corner of the world.
Bottom Line
Remember that following these web standards doesn’t mean that every web browser needs to be a carbon copy of each other.
They could easily differentiate themselves in the UI/UX front, which they provide, among other things. It’s just that their backend functionality needs to be in line with the rules that have been laid down.
Lastly, if you've any thoughts or feedback, then feel free to drop in below comment box. You can also report the outdated information.