The Windows PC has Efficiency Mode, which can reduce the process interference with the task manager. It reduces the power and energy consumption for background tasks.
The Chrome and Edge browsers have integrated their API to make processes energy efficient. To avoid any issues, we can disable the efficiency mode from the Windows Task Manager.
In this guide, I have shared written instruction about:
What is Efficiency Mode?
As a part of Microsoft’s commitment to becoming carbon-negative by 2030, it has launched several features and power management to reduce the overall impact of software. One such feature was the introduction of EcoQoS, which allows developers to run their apps efficiently to improve power consumption and battery life.
EcoQoS is a new Quality of Service (QoS) level introduced to Windows. Developers can now opt-in to run their work efficiently, leading to better energy efficiency/increased battery life, reduced fan noise, and power/thermal throttling.
Google Chrome and Microsoft Edge have adapted this feature and integrated these APIs to utilize Efficiency Mode, which reduces background-process consumption. It’s typically applied to the browser’s sub-processes.
You can check the Windows Task Manager app to see the Eco Mode in action for Chrome, Edge, and other applications that are part of this integration. You will notice a Green Leaf icon next to the processes, indicating it’s running in Efficiency Mode.
However, only some things are going great; there are a few reports that the efficiency mode is causing disruptive browsing, especially the browser getting frozen or stuck for a few minutes as processes run on the low power mode. Hence, leaving no option that turns off the Efficiency mode for the application.
Disable the Efficiency Mode on Windows
The efficiency mode is enabled by default on the Windows PC. If an application like the web browser or any program has been utilizing the EcoQoS API, it will automatically be part of Efficiency Mode. Turning off the mode from the Windows Task Manager app is the only way to stop it.
Note: You cannot permanently disable the Efficiency Mode for the selected processes. It might reappear if you open browsing new tabs or start using extensions; the disabled process stays dormant until you restart the browser or application.
Disable the Efficiency Mode for Chrome app
- Launch the Google Chrome app on your Windows PC.
- Open the Task Manager app from the Start menu.
- Expand the Google Chrome sub-processes.
- Select the Sub-processes with Efficiency Mode (or green leaf) enabled.
- Click on the Efficiency mode command option in the toolbar to deactivate it.
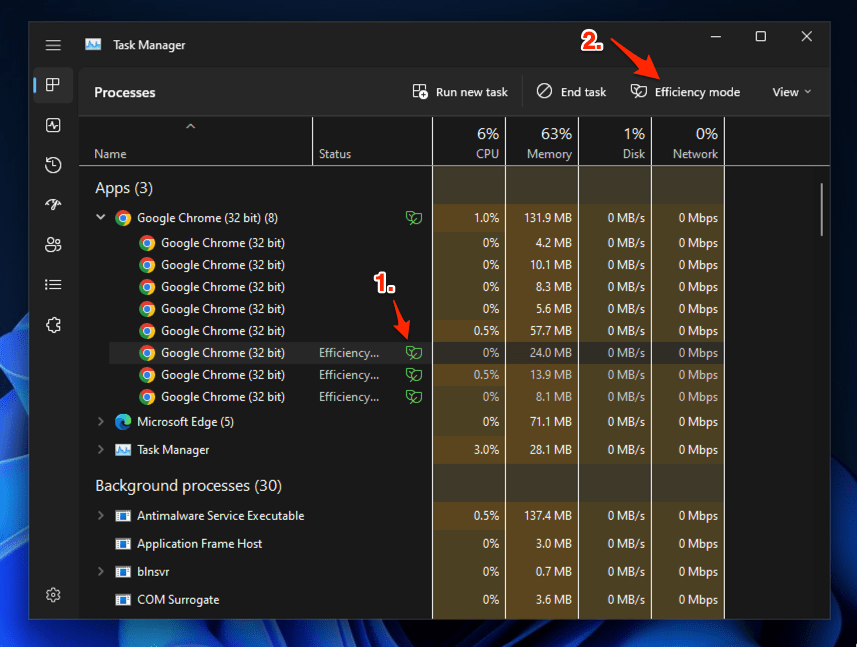
Turn off the eco mode for all other active Google Chrome processes with green leaf to stop using the Windows Efficiency Mode.
Disable the Efficiency Mode for Edge browser
- Launch the Microsoft Edge on your Windows PC.
- Open the Task Manager app and expand the Microsoft Edge app sub-processes.
- Right-click for the context menu where the Efficiency Mode (or green leaf) is visible.
- Select the Efficiency Mode option to uncheck or deactivate it.
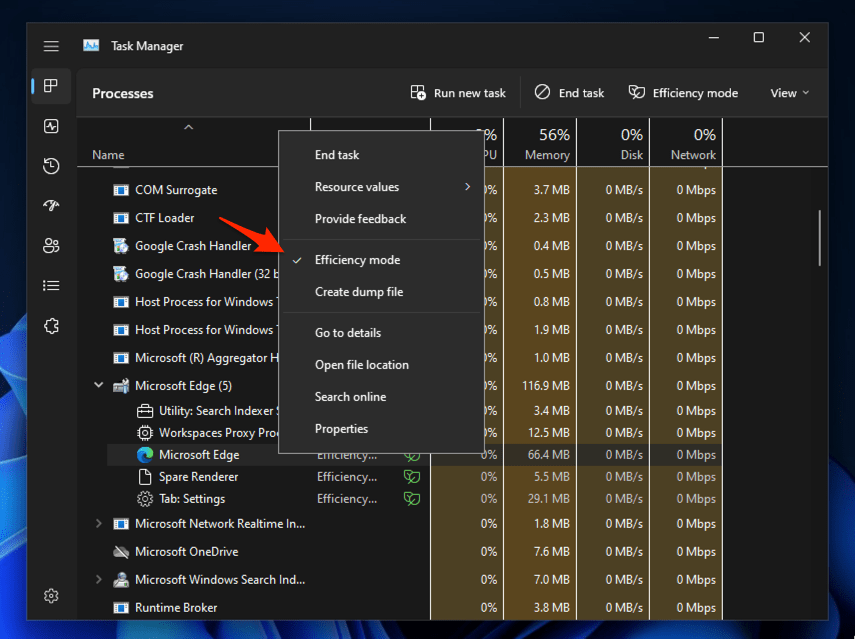
That’s it. The efficiency mode is now disabled for the Edge browser. Similarly, you can disable all other processes under Microsoft Edge.
Another option is under the System and Performance settings within the Edge browser interface. You need to ensure the option is set to Off. Follow these steps:
- Launch the Edge browser on your Windows PC.
- Visit edge://settings/system from the Address bar.
- Under the Optimize Performance section, turn off the Efficiency Mode toggle button.
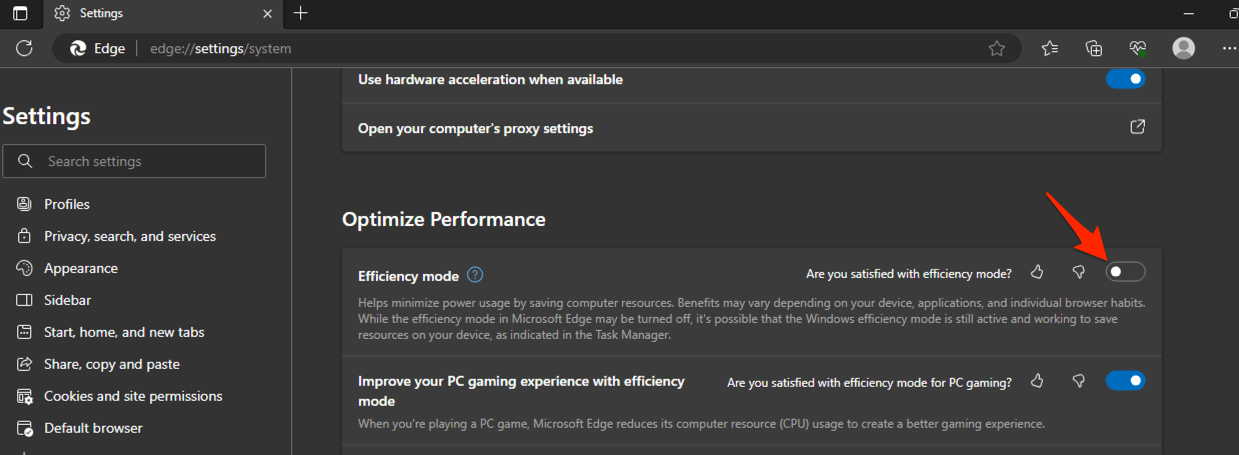
It will disable the Efficiency Mode on the Edge browser and utilize full power and battery to perform the task without glitches.
Alternatives to Disabling the Efficiency Mode
Running the background processes in the low or efficient power mode is a great feature; however, deactivating it completely might not be a good workaround. In cases where you want to take a step forward and try out a few other alternatives to disabling efficiency mode.
Reduce the number of open tabs
If multiple open tabs are running on the browser, then each tab has a memory footprint running in the background. Whether it’s an active or inactive tab, it still consumes the RAM from the system.
Hence, reducing the number of open tabs on your browser can free some space to improve overall browser performance. You can check the memory consumption of each tab from the built-in Task Manager in the browser.
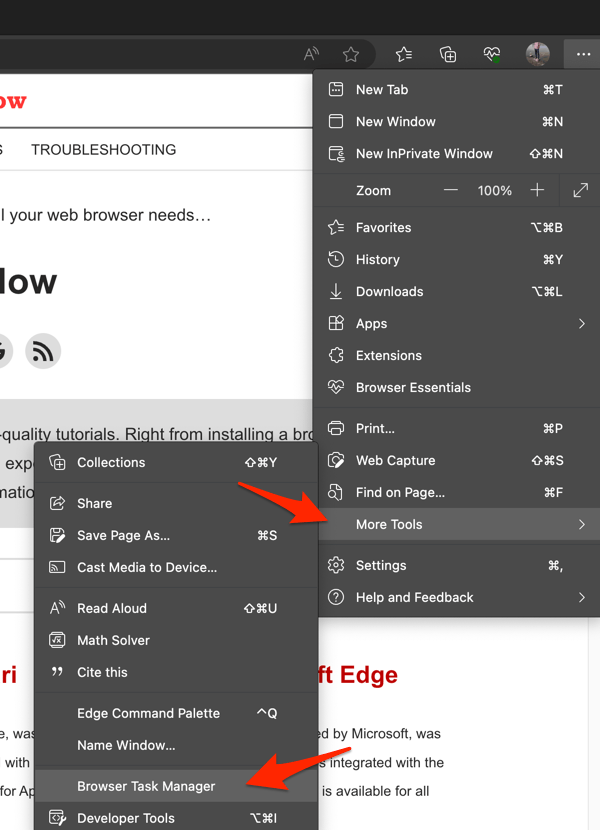
- Open the Chrome (or Edge) browser on your PC.
- Click on the More menu for options and hover on the More tools.
- Select the Browser Task Manager from the list.
 It will launch the built-in task manager.
It will launch the built-in task manager. - Check for the Memory and CPU column of each tab and extension.
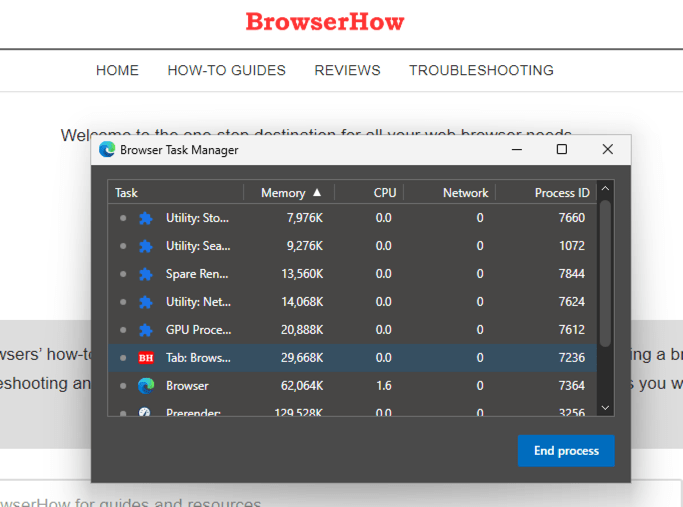
You can select an unused tab or extensions and click on the command button to stop. Use this option cautiously.
Disable the Browser Extensions
Browser extensions use memory and CPU to keep them active even in the background. If you have extensions you do not regularly use, turning it off makes sense to avoid unauthorized memory usage in the background.
You can visit the Extensions page on the Chrome and Edge browser to disable the extensions.
- Open the Chrome (or Edge) browser.
- Visit the Extensions page from the address bar:
- Chrome: chrome://extensions
- Edge: edge://extensions
- Disable the toggle button for the extensions that are not in use.
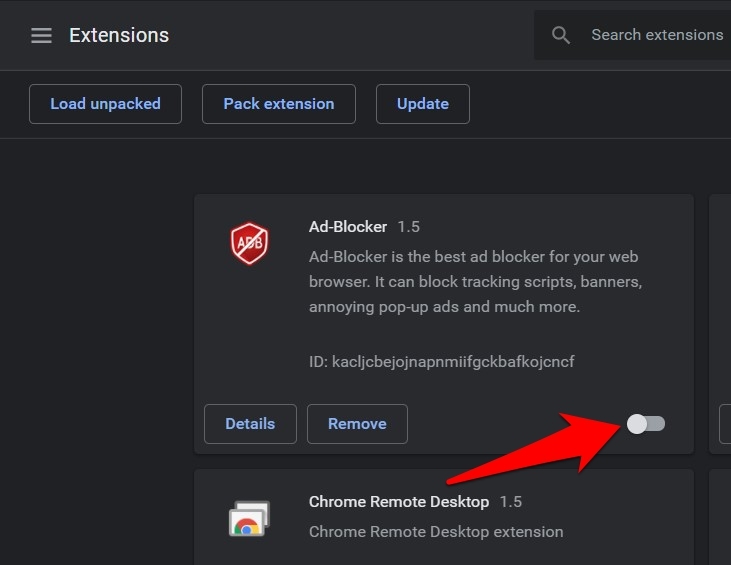
You can always visit the extensions page on the browser to enable it when required. It will save the memory and power consumption.
Enable the Memory Saver in Google Chrome
The Google Chrome browser has the Memory Saver option under the Performance tab on the browser’s Settings page. You can enable this option to free up the memory from inactive tabs and helps other applications and processes use the saved memory. Here are the steps to enable it:
- Launch the Google Chrome browser.
- Click on the More
 options menu.
options menu. - Hover on the More Tools option and select the Performance menu.
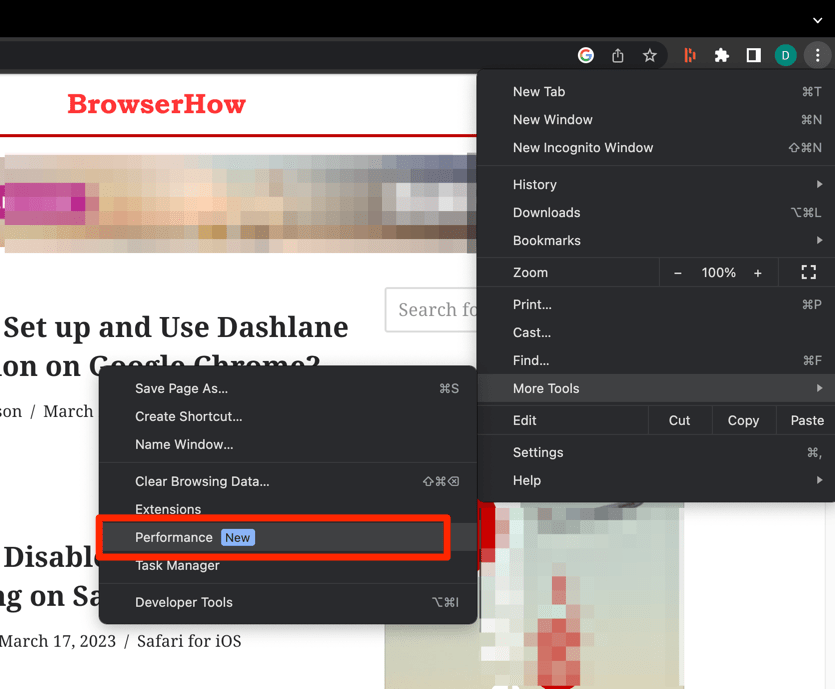 It will launch the Performance tab under the Chrome Settings page.
It will launch the Performance tab under the Chrome Settings page. - Enable the Toggle button for the Memory Saver option.
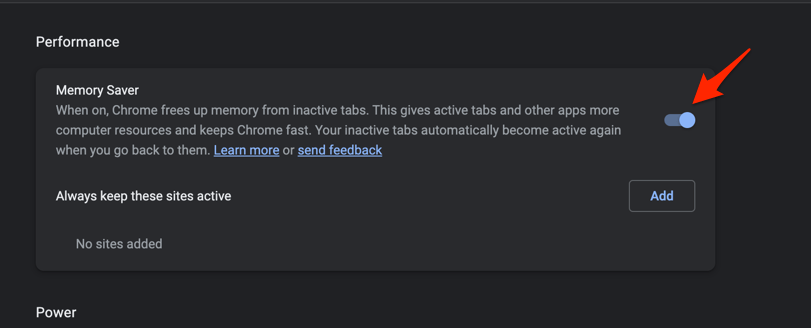
The Chrome browser also has the Energy Saver option, but it’s unavailable for Windows since it uses the Efficiency Mode as an alternative to the battery saver.
The Edge browser does not have a memory saver or energy saver option. However, it utilizes Windows’s Efficiency Mode for the same. You can configure by visiting the System and Performance tab, as mentioned previously; however, instead of turning it Off, you need to turn it On.
Bottom Line
There is no doubt that efficiency mode is a good feature for the Windows application to run on low power and improve the overall sustainability to turn carbon negative. However, the feature might be overly optimizing the processes resulting in issues.
If you think disabling the Efficiency Mode is the ultimate solution for Chrome and Edge to stop freezing while switching tabs or moving windows, then you should turn it off. Though it’s temporary, but works well in some cases.
Lastly, if you've any thoughts or feedback, then feel free to drop in below comment box. You can also report the outdated information.