High CPU usage in the Firefox browser is mainly due to the parsing of heavy website elements and background processes.
It can be fixed by tweaking browser configuration and avoiding using many third-party add-ons running in the background. You can also clear the cache and adjust the Firewall settings to reduce CPU usage.
Many concerned users have posted the same query across various Mozilla Support Forums.
In this guide, I have shared written instruction about:
Method 1: Update Firefox to the latest version
If the browser is outdated, there can be issues with Firefox compatibility. We should check for the latest updates and proceed with the same.
- Open the Firefox browser app on your computer.
- Click on the More
 menu and select the Settings menu.
menu and select the Settings menu.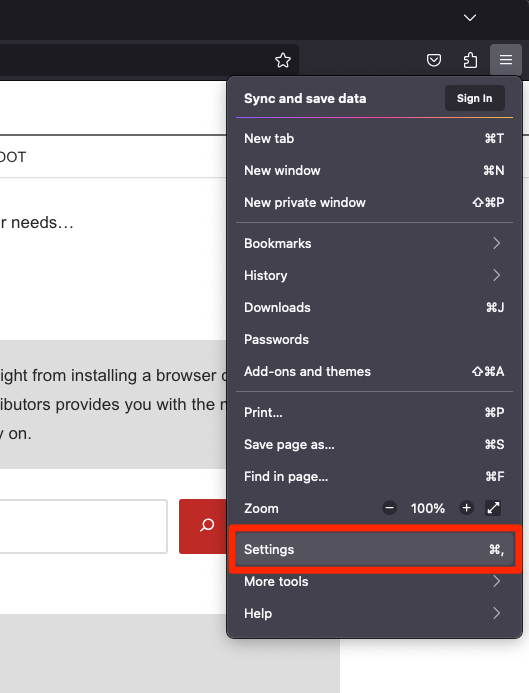
- Scroll down to the Firefox Updates section within the General tab, and click the button.
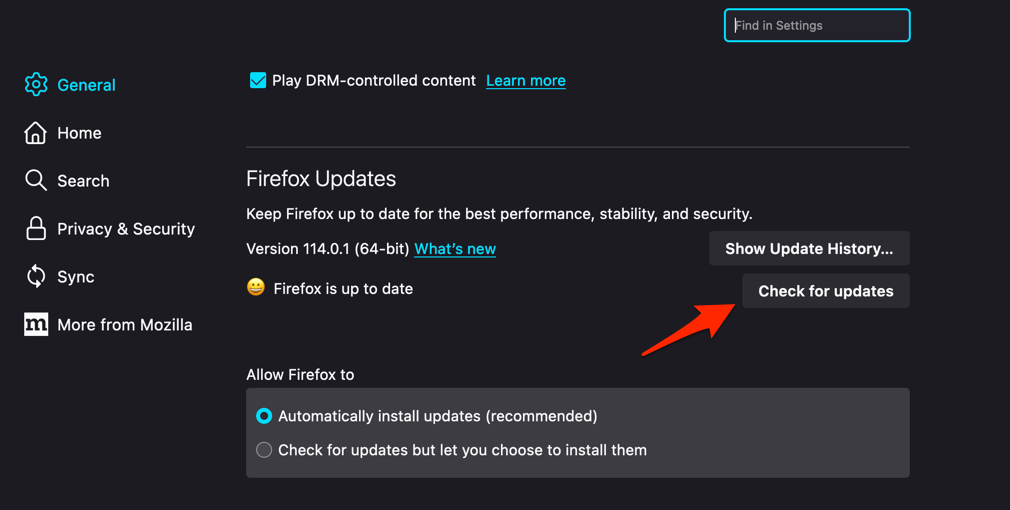
- Firefox will check for updates and download them. It may ask to restart to complete the installation of the update.
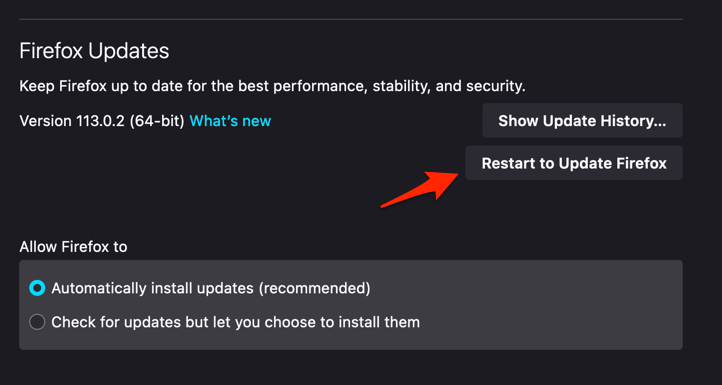 The browser will be updated to the latest version.
The browser will be updated to the latest version.
After the update, check the task manager to see if CPU usage has returned to normal.
Method 2: Boot Firefox to Safe Mode
Booting the browser to Safe mode will turn off all third-party add-ons and themes. So, if the browser performs along the expected lines in this mode. Hence, it would be best if you considered disabling it. Here are the steps for enabling safe mode:
- Launch the Mozilla Firefox browser
- Click on the Menu
 at the top right.
at the top right. - Select Help > Restart With Add-ons Disabled from the drop-down.
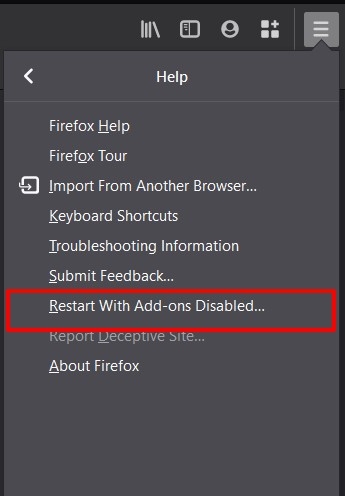
- This will launch the browser in Safe Mode.
Check how it is performing now. If you notice considerable improvement, boot the browser back to normal mode and uninstall the recently installed extensions, one at a time, until the performance issue is rectified.
While third-party add-ons add more browser features, they could cause a few issues. In those cases, removing them and looking for alternatives is best.
Method 3: Use Strict Tracking Protection
Firefox has three levels of tracking protection: Standard, Strict, and Custom. The Strict one is known to block most trackers, cookies, and content across various sites. This, in turn, might also speed up the loading time of various sites, so you could consider enabling it.
- Launch the Firefox app on a computer.
- Click on the Menu
 and select the Options menu.
and select the Options menu. - Switch to the Privacy and Security section from the left menu bar.
- Select the Strict mode from the Enhanced Tracking Protection section.
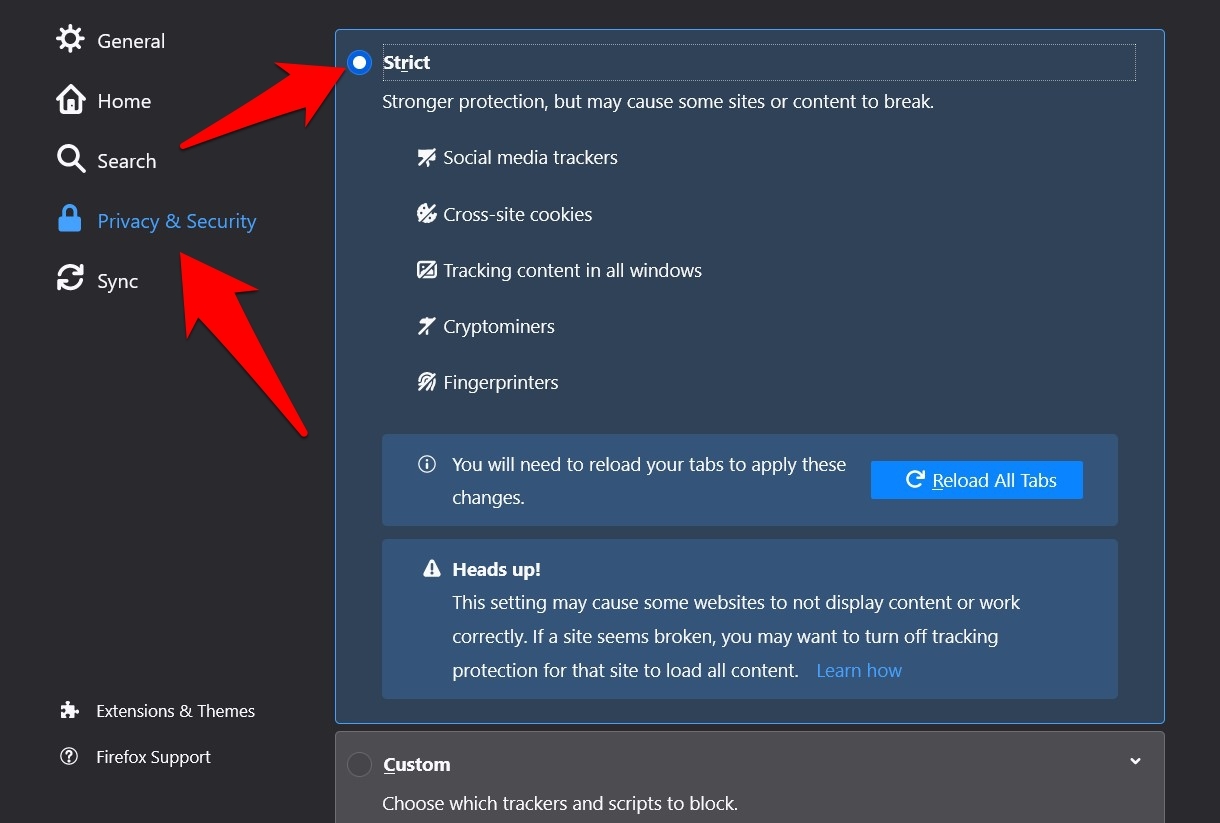
One of the most significant drawbacks of the Strict Mode is that its heavy protection mechanism could break some websites and their contents.
Method 4: Enable Hardware Acceleration
Firefox uses your PC’s primary process when dealing with graphics-intensive components. However, other apps might be unable to make optimal RAM usage and could slow down the entire PC. Therefore, consider instructing the browser to use the PC’s graphics processor rather than the main one using the hardware acceleration feature.
- Launch the Firefox browser on a computer.
- Click on the Menu
 and select the Options menu.
and select the Options menu. - Scroll to the Performance section under the General tab.
- Uncheck the Use recommended performance settings option.
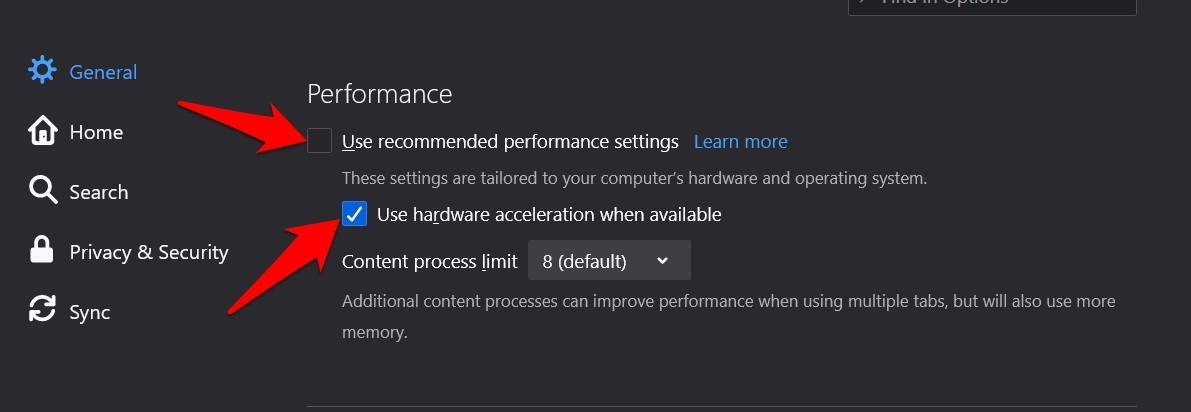
- Enable the Use hardware acceleration when available option checkbox.
See if it fixes the high CPU usage issue. The hardware acceleration feature depends on the graphics processor, so a weaker chipset might not offer preferable mileage.
Method 5: Decrease Content Process Limit
By default, Firefox allocates the maximum available content process. This makes it easier for the browser to deal with multiple opened tabs simultaneously. However, it also leads to more RAM consumption. Hence, you could consider decreasing its value for optimum RAM usage.
Here are the steps to reduce the content process limit:
- Launch Mozilla Firefox on a computer.
- Click on the Menu
 and select Options.
and select Options. - Scroll to the Performance section under the General tab.
- Uncheck the Use recommended performance settings option.
This shall bring up the Content process limit drop-down menu. - Change the value from 8 to something lower, say 4.
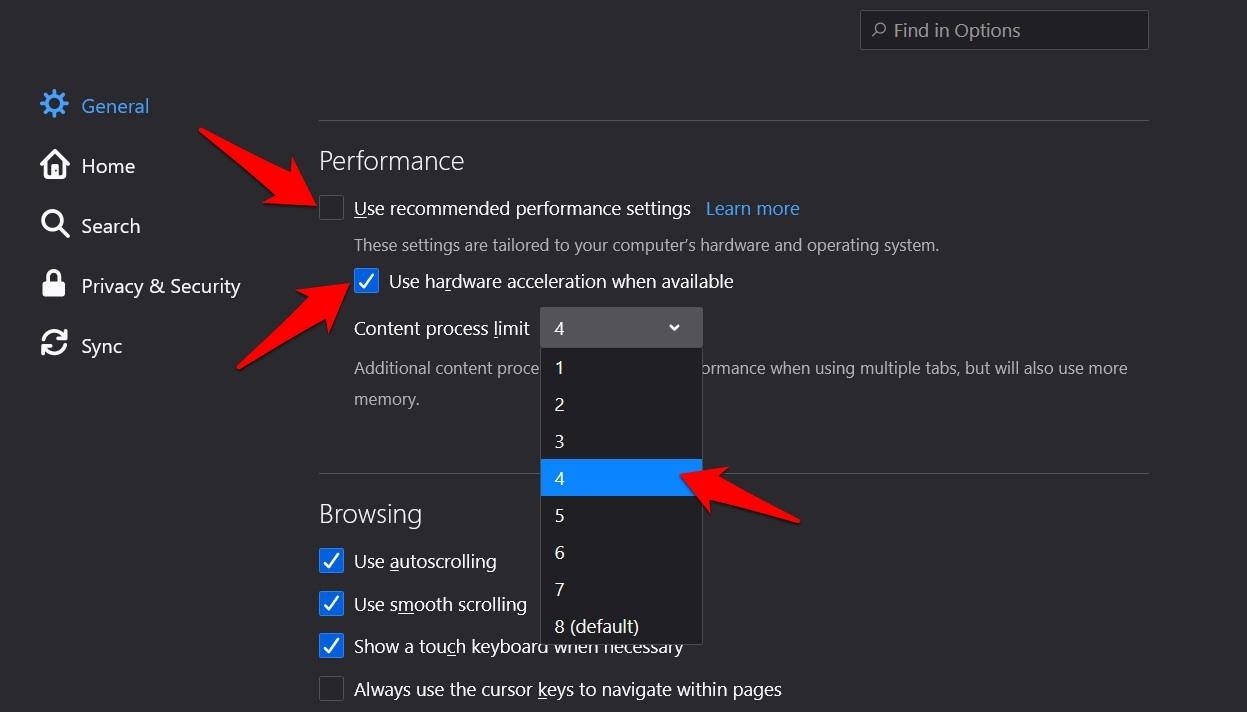
Restart Firefox and check whether the CPU usage issue has been settled. Decreasing the content process limit might give you a hard time dealing with multiple tabs simultaneously.
So, consider keeping the number of opened tabs at a lower level.
Method 6: Delete content-prefs.sqlite file
The content-prefs.sqlite file beholds data related to the user profiles. However, if any data gets corrupted, it could harm the browser’s overall performance. So, it is recommended that this file be deleted and Firefox automatically creates its new instance.
- Launch the Mozilla Firefox browser.
- Click on the Menu
 at the top right.
at the top right. - Select the Help > Troubleshooting Information option.
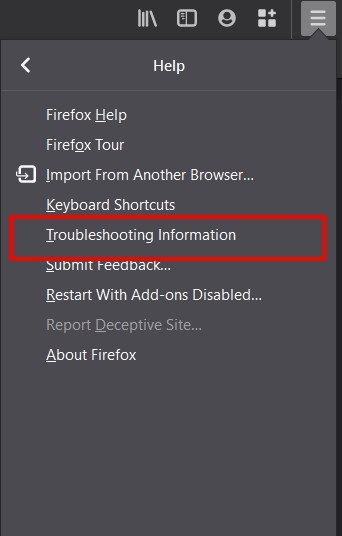
- Within the Application Basics section, go to Profile Folder and click on the button.
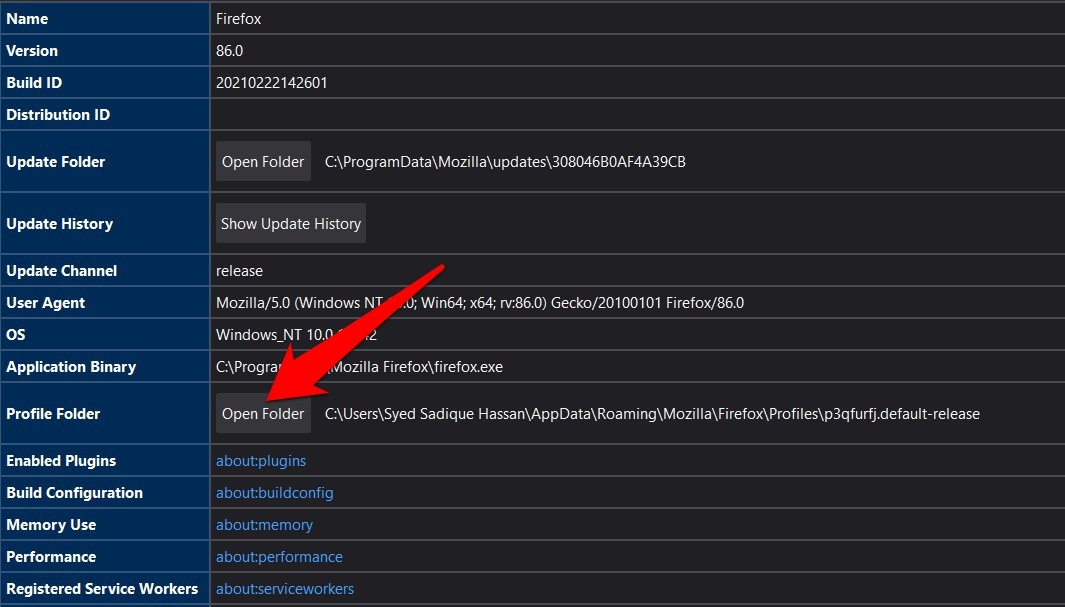
- Select the content-prefs.sqlite file and Delete it.
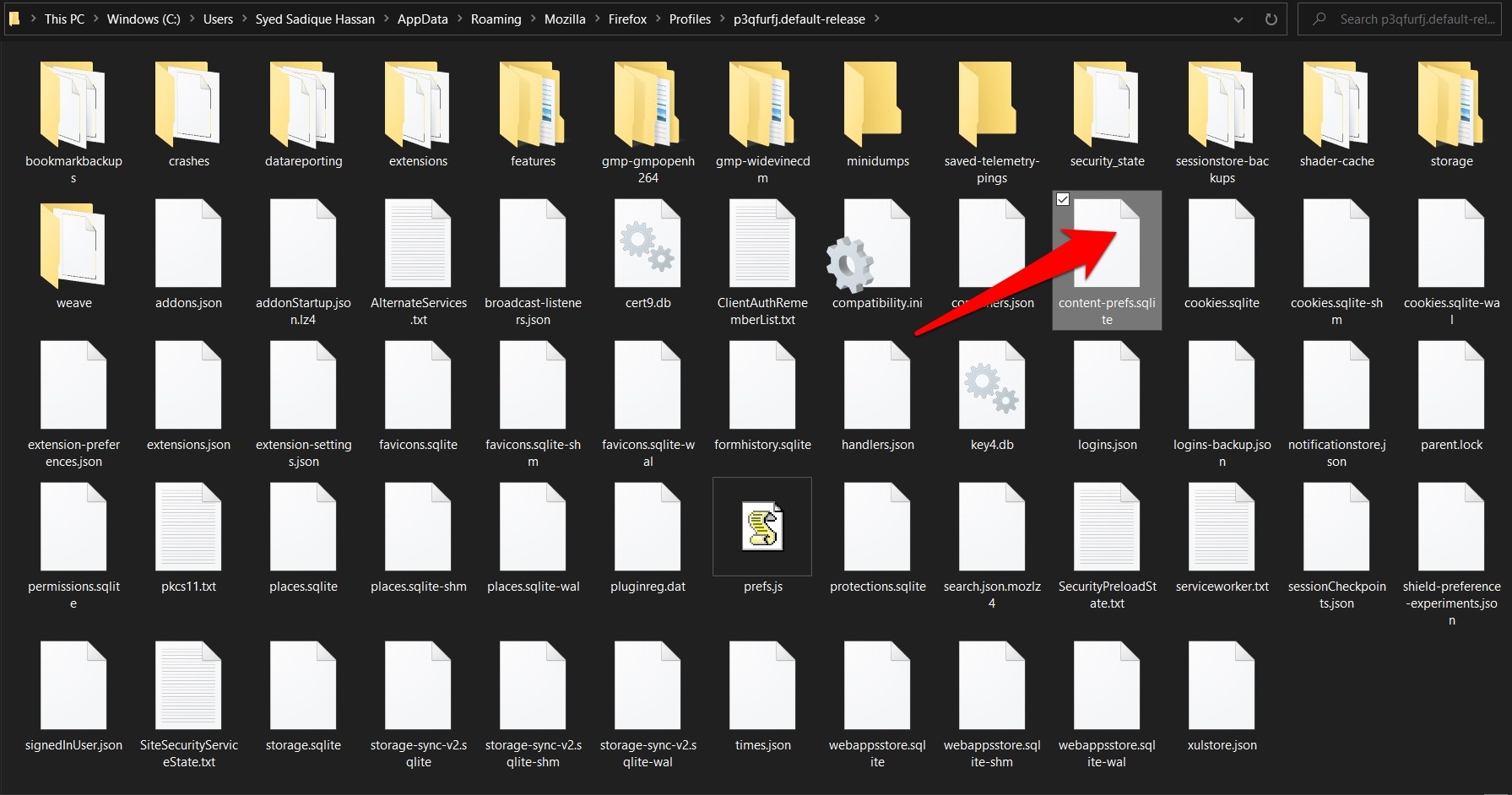
Once you’ve done this, restart the browser and see if resource consumption has been minimized. Upon deleting the above file, you might notice some settings that are not synced with your preferences. So make sure to set them accordingly.
Method 7: Refresh (or Reset) Firefox
Note: Firefox Reset will remove all the third-party add-ons and customizations you made to the browser. However, your data (bookmarks, passwords, etc.) will stay safe.
Here are the steps to reset:
- Copy-paste about:support in the Firefox address bar, and hit key.
It shall take you to the Troubleshoot page. - Click on the button is situated at the right.
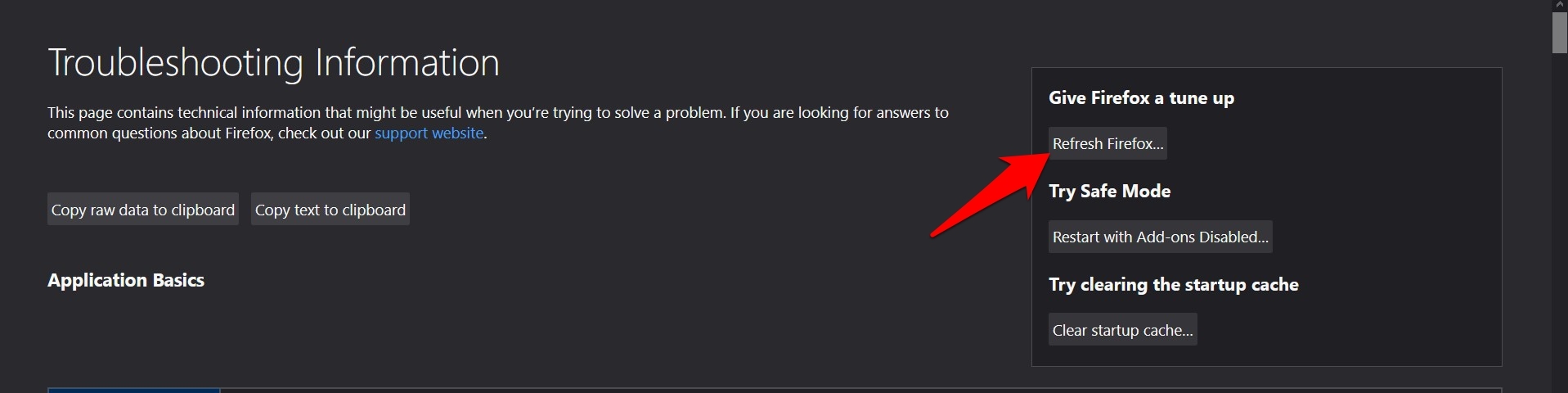 It will open a dialog box for confirmation.
It will open a dialog box for confirmation. - Hit on the command button.
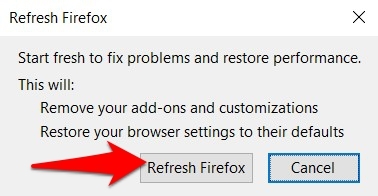
- Wait for the process to complete and Relaunch the Firefox browser.
Upon carrying out these steps, you will lose all the installed extensions and configurations you made to the browser.
Bottom Line
Installing some third-party extensions kept the browser’s processes up and running all the time, leading to high resource consumption. So, by booting the browser to Safe Mode, we could identify the add-ons causing the problem.
If none of the above fixes work for you, you should consider switching to an alternative browser for your computer. We have already listed the best browsers for Windows and macOS.
Lastly, if you've any thoughts or feedback, then feel free to drop in below comment box. You can also report the outdated information.







I tried all of the steps outlined above, including “Refresh Firefox”. They may have mitigated the performance issue but Firefox is still a CPU hog, even when not accessing the web at all and without any tabs open (except for the default home page).
I was trying to diagnose issues with Windows and a laptop that had freezing issues. So I installed Ubuntu 22.04LTS. When running Firefox or Edge browser I experienced strange spikes with CPU. Although the spikes would affect one core at a time or move from a virtual core to a logical core. At first I thought maybe it was due to fractional scaling, so I went back to 100% scale. Still saw random 100% spikes with cores and fan would max out. Temps would go from 40c to 80c in an instant. I tried re-applying thermal paste which reduced idle temps from 40c to 35c so I knew it was effective. Mind you this is only a 10th gen. Core i3 10110u dual core CPU. After awhile I noticed the spikes also was causing the laptop to freeze up as well. Telling me, there was some serious heat issues.
Hi John, is your system running on the SSD or HDD? Generally, the mechanical HDD has a major effect on the system’s performance, causing the over usage of CPU for minimal activity. SSD makes the overall system smooth and irons out all the CPU-related issues.
Firefox Version 90 – et al….It’s becoming a part time job, Firefox work-arounds….
In the interim, I did a simple .bat that I use every time I exit Firefox. It immediately kills the 9-12 hoggy processes that keep running long after you exit the browser. I’ve had no mal-effect from using this. The browser opens/operates rapidly and predictably afterward. Also this immediately frees up my resources so that I can…jee.. actually USE my computer after a session on Firefox.
To make your own:
1. Open Notepad & type or copy/paste from here:
taskkill /F /IM firefox.exe
2. Save it as the default .txt file with any name that is meaningful to you… “Parasite.txt” whatever… Locate this file you just saved, right click and select “rename.” Change the file extension (last three characters) from “.txt” to .bat.
– if you want to get swoopy, create an icon for this (right click) and put it on your desktop for handy access.
To use:
Every time you close Firefox, double click on either the .bat file you created or your swoopy icon. It assassinates all of the active and running Firefox.exe processes in a blink.