Attackers can inject malware into the Apple Safari browser, resulting in activities like different search engine engines, website loading issues, malicious ads, and pop-ups.
However, we can remove these malware injections easily after resetting the browser data, settings, and extensions back to normal.
In this guide, I have shared written instruction about:
Method 1: Check Malware Attack
Whenever malware enters your system, it will create certain disturbances and abnormal behavior in your Safari browser. It may redirect you to different pages suddenly and display unwanted pop-up ads out of the blue.
One such example of a potential threat to Safari is the Bing and Yahoo redirect virus and Search Marquis which dominated for a long time in 2019. It is used to redirect the user’s internet traffic to the front page of being without any permission.
And even if users successfully identified the potential threat, no one could understand its purpose or how to check for it.
Method 2: Remove Suspicious Browser Extensions
The primary source of malware in the Safari browser is due to third-party extensions or plugins. These extensions get automatically installed when you visit a questionable downloading website. And as a result, they either show advertisements or use your browser performance power to mine cryptocurrency.
Either way, it’s hard to find them, but the best way to deal with such suspicious extensions is to delete them.
- Open the Safari browser app on your Mac.
- Click on the Safari menu and select the Preferences/Settings sub-menu.
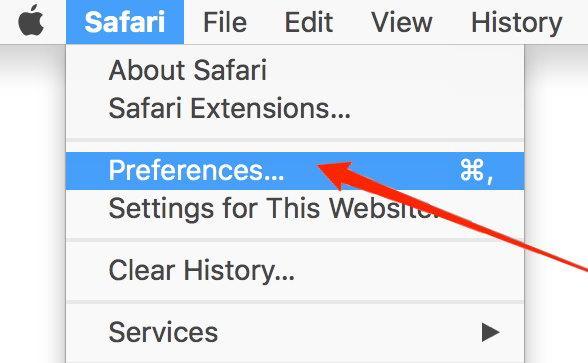 It will open the Safari Preferences window.
It will open the Safari Preferences window. - Switch to the Extensions tab.
- Lookup for suspicious extensions installed.
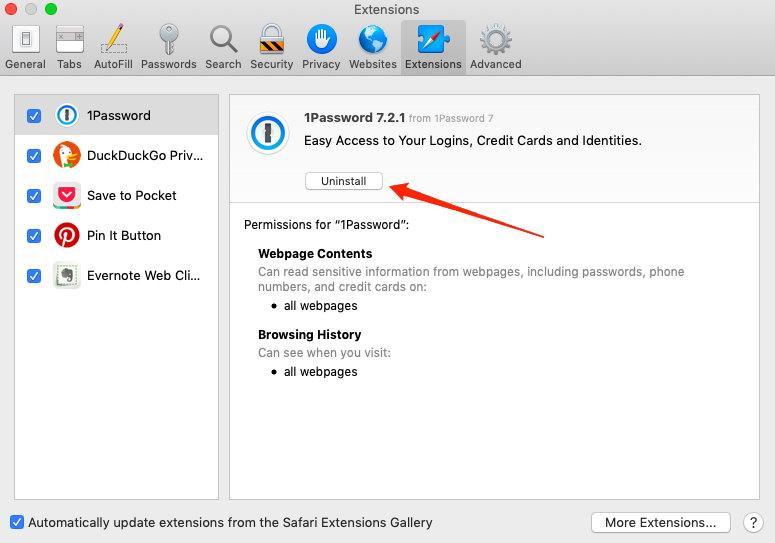
- Select the extension, and hit to remove it from Safari.
It will immediately remove the extension and make the browser less vulnerable. However, the extension might already make changes in settings; it is better to check and reset the options to a normal state.
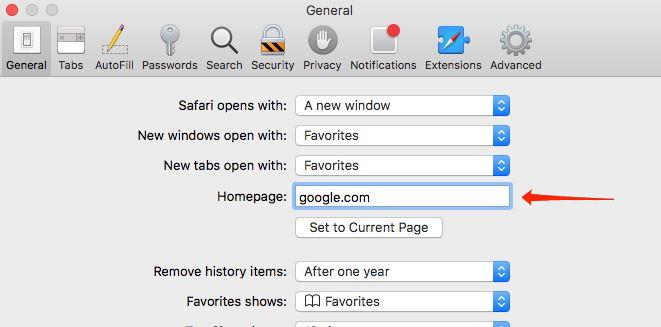
Under the same Safari preferences window —
- Switch to the General tab, and set a preferred homepage for your Safari browser.
- Again, switch to the Search tab, and set your default search engine.
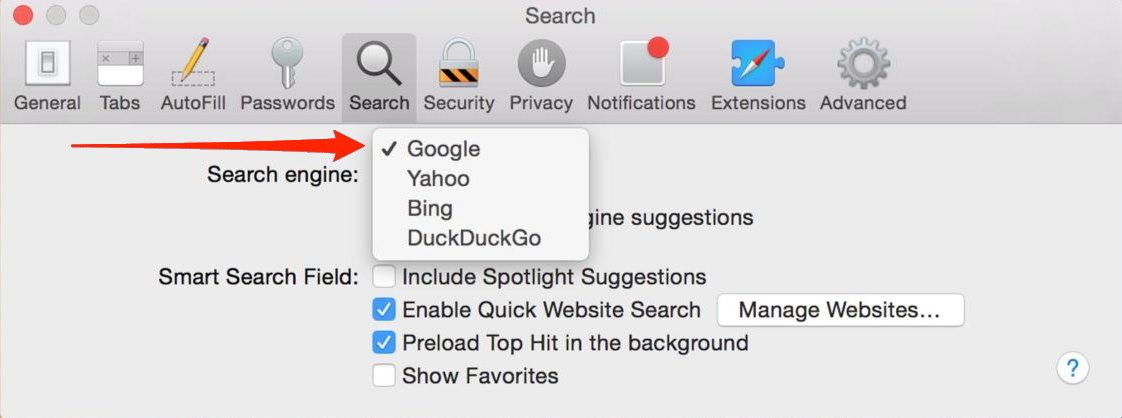
Restart the Safari browser and check if the problem doesn’t appear anymore. However, if the problem persists in your browser, try the following method on our list.
Method 3: Reset to Safari to Default Settings
Extensions come with special privileges and permissions so that they can alter the setting of your Safari browser. This, in turn, shows suspicious behavior such as unnecessary ads, slow web pages, etc. Resetting Safari settings on your Mac will delete any malicious configuration injected by the malware.
Follow the steps to reset Safari settings to the Default:
- Launch the Finder window on Mac.
- Press the key and select the Go menu.
- Select the Library option from the drop-down menu.
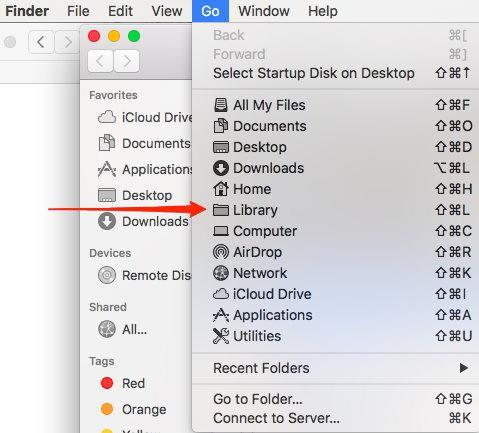
- Navigate to Library > Preferences folder.
- Delete com.apple.Safari.plist file from the preferences folder.
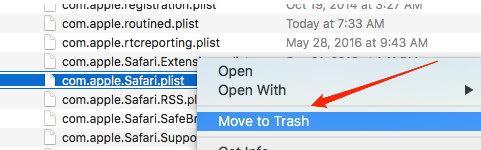
We have deleted the default configuration file. Just restart the Safari browser to regenerate the new configuration file we deleted. It should clear any malware injections.
Method 4: Clear Browser Cache and History
The cache is a temporary storage solution for the browser, which helps Safari load certain web pages faster. But if the malware is hiding in the cache files, it will create a problem even after you reset or delete your browsing history.
Furthermore, a filled cache memory may slow down your website performance, so clearing the browser cache every six months is a good practice. Here are the steps to clear browser data:
- Launch the Apple Safari browser.
- Click on the Safari menu and select the Preferences sub-menu.
- Switch to the Advanced tab.
- Enable the check box for the Show Develop menu in the menu bar.
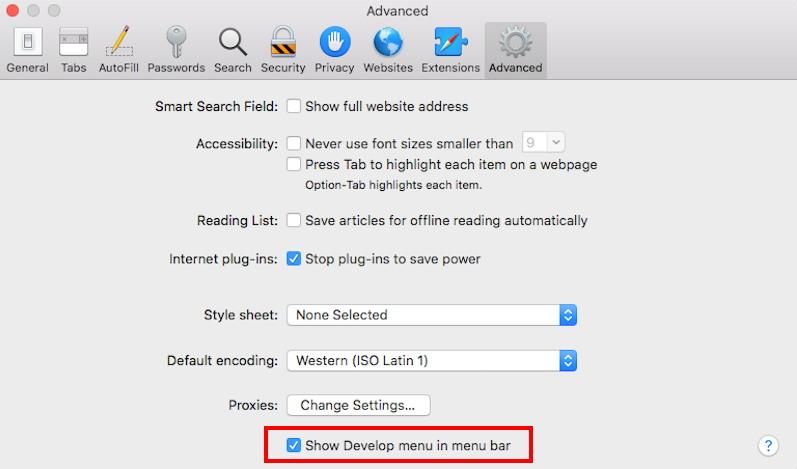 It will enable a new Develop menu in the Safari menu bar.
It will enable a new Develop menu in the Safari menu bar. - Click on the Develop menu on the menu bar.
- Select Empty Caches from the drop-down menu.
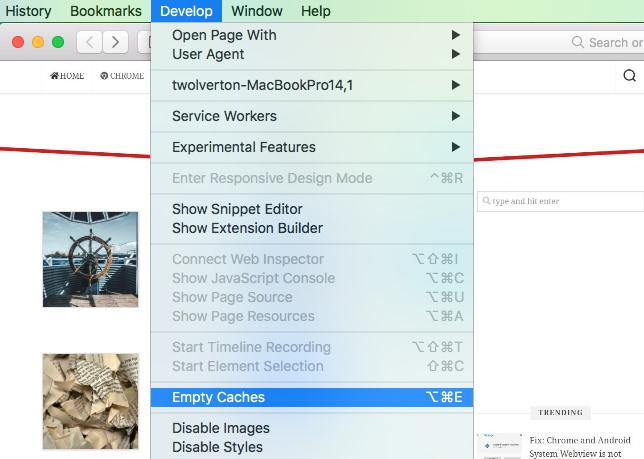 It will clear and empty all the cache files stored within the Safari browser.
It will clear and empty all the cache files stored within the Safari browser. - Next, Click on the History menu on the menu bar.
- Click on the Clear History… option.
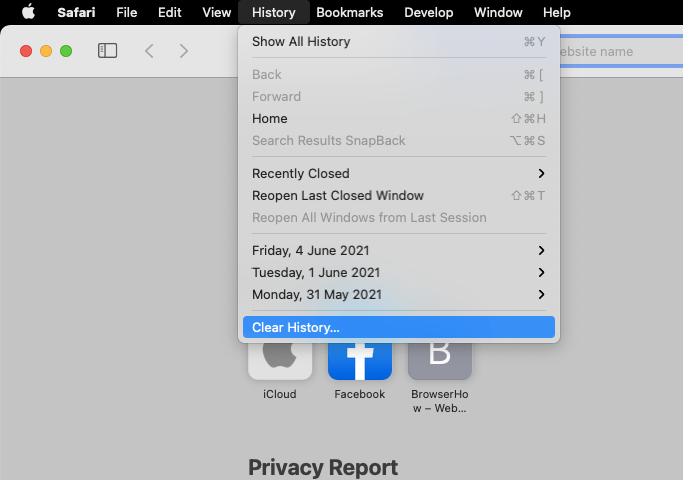 It will display a clear history dialog box on the screen.
It will display a clear history dialog box on the screen. - Choose a suitable Time Range and click the button.
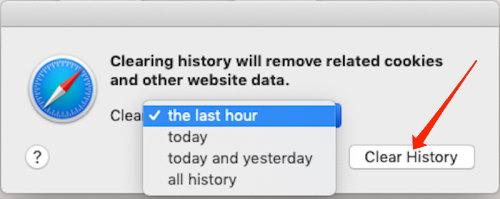
TIP: Choose the “All history” option for the best results. However, it will wipe out the complete browser history.
Method 5: Manage and Delete Website Data
Website data comprise special features such as cookies and browsing or behavior patterns. These might also include your log-in sessions or other website identifiers.
If your browser is infected with malware, it can grab sensitive information via website data, so it is good to delete it. Here are the steps to delete Website data:
- Launch the Apple Safari browser.
- Click on the Safari menu and select the Preferences sub-menu.
- Switch to the Privacy tab, and click on the button.
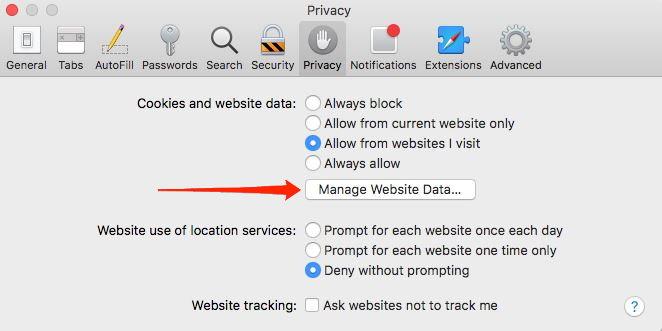 It will open the stored website data and cache.
It will open the stored website data and cache. - Hit on the option.
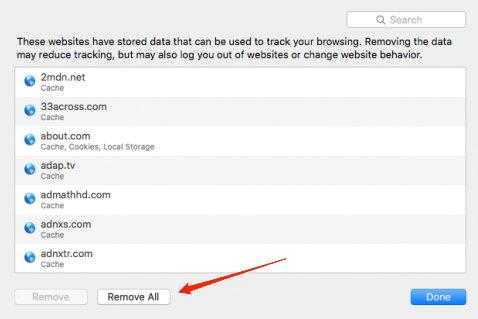
- Click on the button.
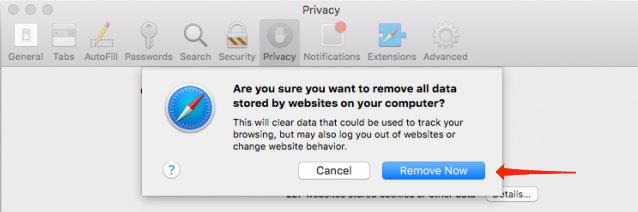
It will delete all the stored website data and cache files from the Safari browser.
Bottom Line
Malware can be attached to our system and browser app without our knowledge. They modify the browser settings and inject different scripts to continue hijacking.
We need to first identify different files and folders the malware was injected within our system. We can use the third-party apps for the same.
Post that, we can check for browser extensions, changes made to settings and reset the Safari app preference list to delete all configuration. Clearing the cache and website data should help in complete wipe out of malware from browser app.
Lastly, if you've any thoughts or feedback, then feel free to drop in below comment box. You can also report the outdated information.



Can you help? Safari keeps trying to load certain websites. Firefox is working OK. I am running Catalina 10.15.7 and the latest Safariu
Hi Ray, Catalina was quite buggy for most users including us. Please consider upgrading to Big Sur or the latest Monterey.
Please follow this article to troubleshoot and fix Safari auto-reloading issues.