The best ways to browse sites privately and safely on any web browser are to select a privacy-enhanced browser, opt for a private browsing mode, use a VPN or proxy server, tweak the browser’s privacy settings, and disable extensions.
In this guide, I have shared written instruction about:
Tip 1: Select a Privacy-Focused Browser
First, if a private and secure browsing experience is at the top of your priority list, you should choose a browser that respects these factors. And one shouldn’t look any further than Tor.
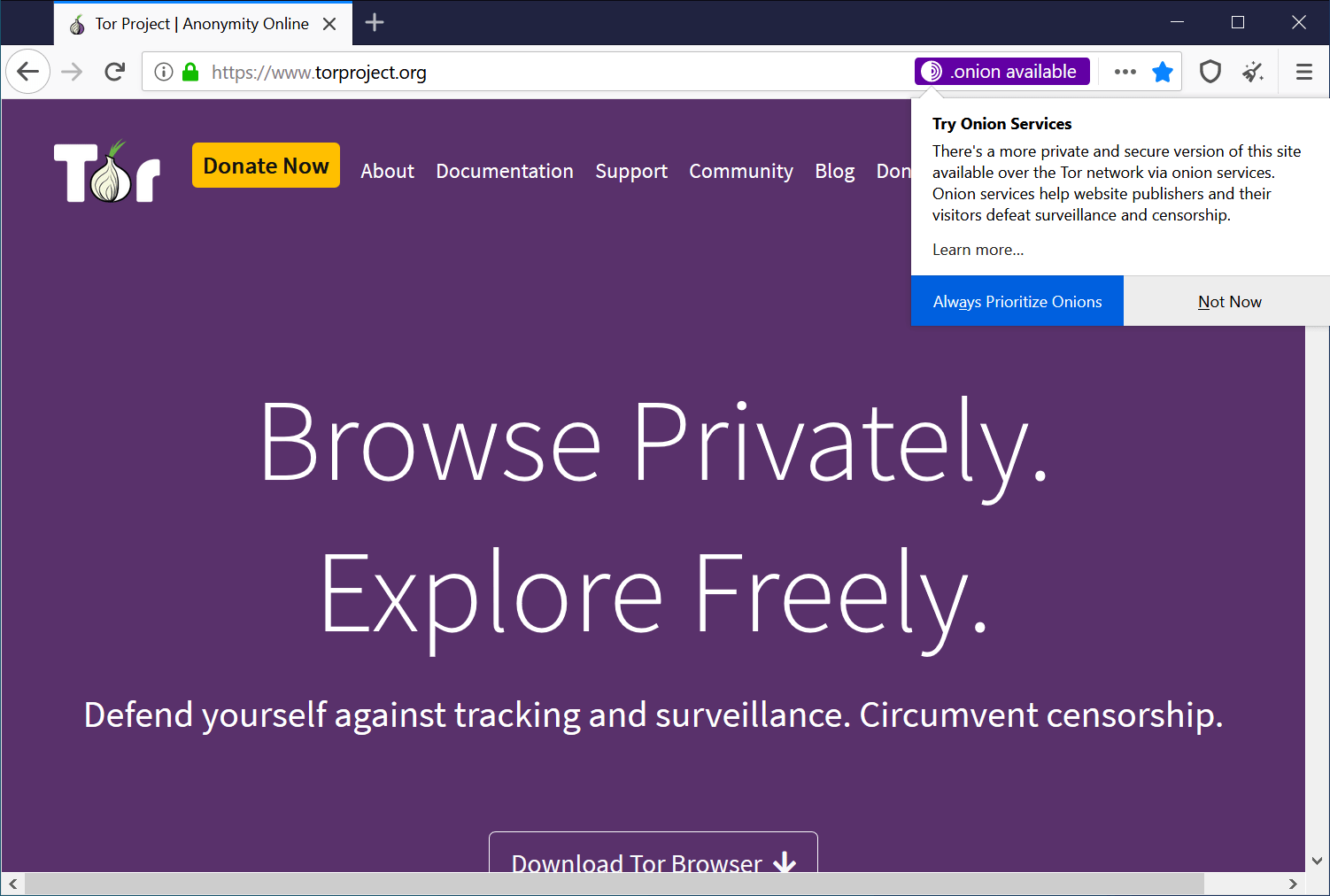
Providing three levels of encryption, it passes all the data via random nodes before taking it to the intended destination. However, all this might come at the cost of a tad outdated UI/UX experience.
So, if you want a more balanced option, opt for the Firefox browser.
Tip 2: Use the Private Browsing Mode
Private mode is in Safari, incognito is in Chrome, or private is in Firefox; while the name may vary, their goals stand the same. These modes offer a more secure browsing experience as they won’t record your browsing history, cookies, session data, or the information you share on other sites.
However, this mode only secures your local privacy by storing these data locally on your PC. When it comes to online security, they aren’t a good alternative, as your browsing activities would still be visible to your ISP and network administrator.
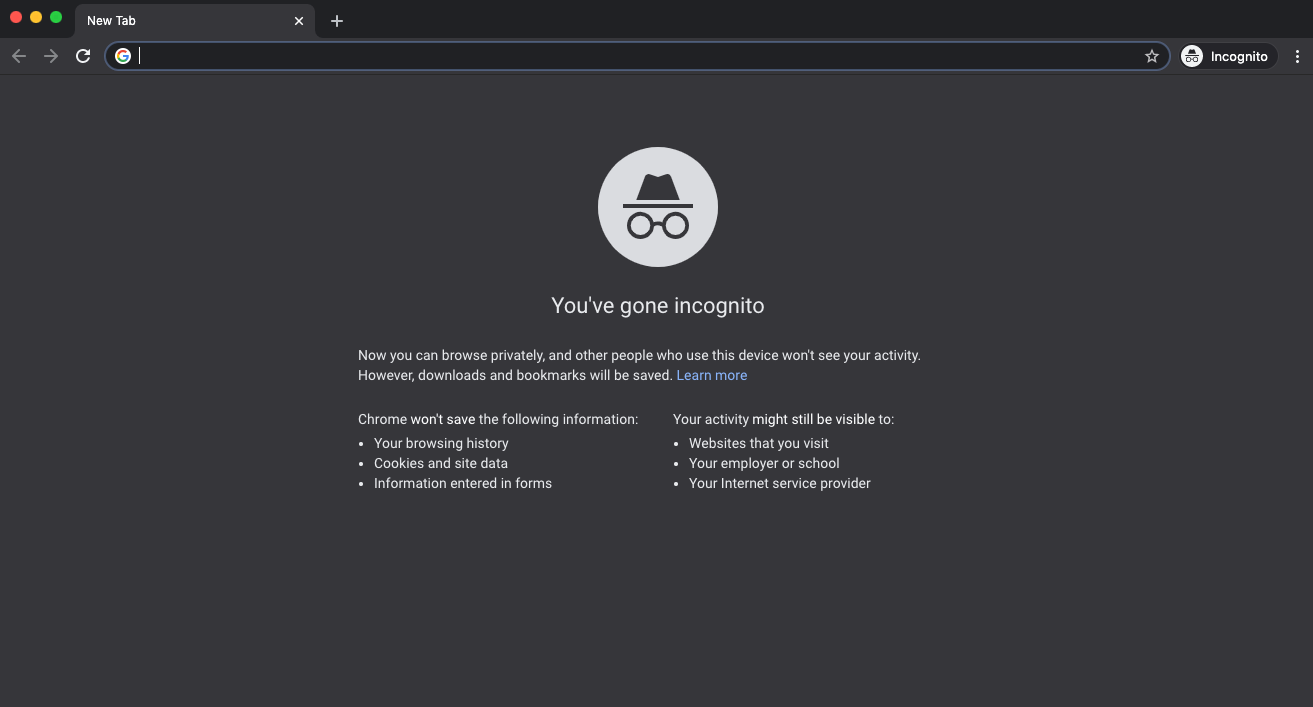
So, for a much safer approach, consider using a proxy or VPN, as mentioned in the subsequent sections.
Tip 3: Use a VPN Connection for Network
A Virtual Private Network creates an encrypted tunnel for the data transfer. Furthermore, as soon as you connect to a VPN server, your original IP address will be disguised to that server; hence, your location remains secure.
So, a VPN becomes necessary if you are looking for a secure and anonymous browsing experience.
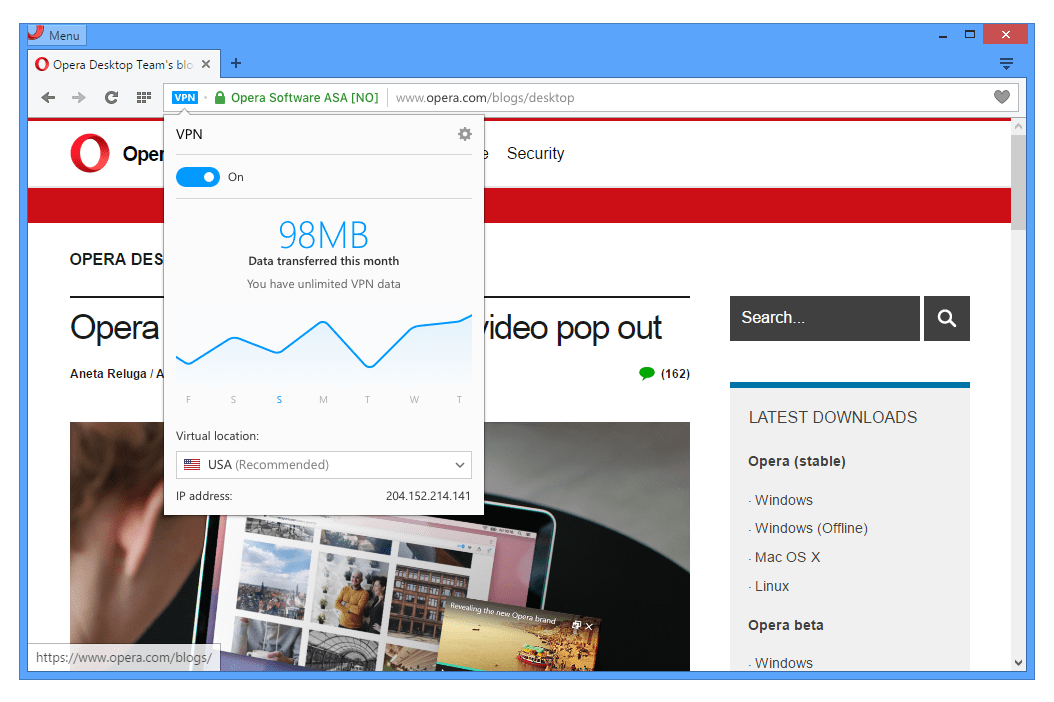
In this regard, there are standalone VPN apps that you could try out. Or even better, some browsers, such as Opera, have a built-in VPN activated.
Tip 4: Use a Proxy Server on a Computer
Now that we are discussing VPNs, let’s take a moment and talk about its other half, Proxies. These act as an intermediary between the client and server and can transfer data on your (client’s) behalf.

While they don’t encrypt the data exchange process like VPN services, they could still be helpful if you browse anonymously on an application level rather than the entire operating system level.
Tip 5: Tweak the Browser’s Privacy Settings
Web browsers come with different levels of privacy, which, by default, is set to a balanced/standard level. While it may suffice for everyday usage, it only translates to the most secure one.
Fortunately, you could easily change the security level and opt for extreme privacy, which Firefox – about:preferences#privacy and Edge – edge://settings/privacy likes to call the Strict Mode
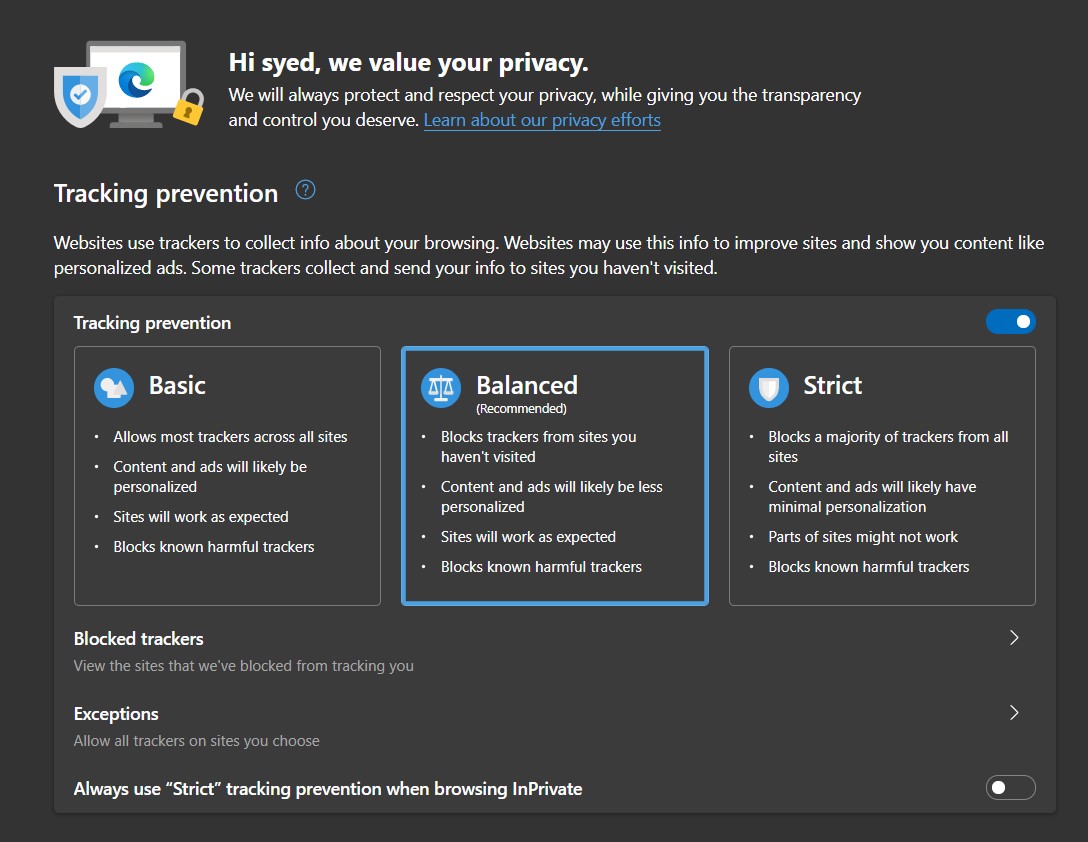
Once enabled, it will block nearly every tracker and script and even stop cookies from collecting data. However, it could also break some site components, and the ones dependent on Java scripts are known to suffer the most.
Tip 6: Disable the Browser Extensions
Extensions are small software programs that add more functionality to your browser. However, they could be giant red flags whenever the question of the browser’s privacy arises.
This is because, for most harmful trackers or programs with malicious intents, the path to enter your browser is usually via the extensions gateway. So, the safest bet is to remove all the installed extensions.
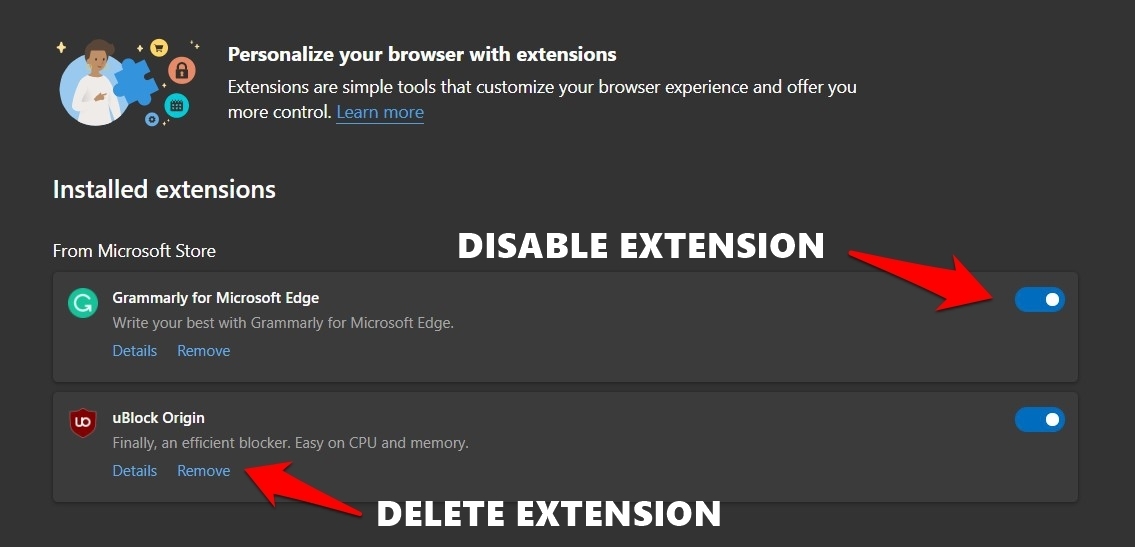
Or if that’s way too aggressive, you should consider removing the ones that need to be from trustworthy developers. Likewise, you could also review those extensions’ user reviews to get an honest opinion.
We already have a guides to disable the extensions:
Bottom Line
You could browse sites privately and safely on the web browser of your choice. As you might have noticed, there’s no universal method; you must combine two or more to get a secure browsing experience.
Lastly, if you've any thoughts or feedback, then feel free to drop in below comment box. You can also report the outdated information.